Table Of Content
Then the part must be flipped from side to side to machine all of the features. The geometry of the features dictates whether the part must be flipped over or not. The more ops (flip of the part), the more expensive the part because it incurs substantial set-up and load/unload time.
Design for Manufacturing With 3D Printing
Virtually all engineering disciplines use DFM, although its implementation varies significantly according to the manufacturing technology. Manufacturing processes such as those used in a printed circuit board (PCB) have guidelines for DFM practices, including specific rules, checks, and tolerances. For example, choosing injection molding for products that will be produced in small volumes is not sustainable due to the huge upfront investments and overheads. In such cases, one may prefer additive manufacturing or thermoforming processes. These processes enable cheaper manufacturing with fewer parts rather than having to make a huge investment in molds and tools.
Advancements in DFM Techniques and Technologies
From the many methods under DFX, designers choose one or more that are relevant to their product design objectives. Then, by implementing the principles under each of those methods, the designers can ensure an excellent product design. In the case of aluminum as an example, bar stock and plate are the two most common forms from which machined parts are made. The size and shape of the component may determine which form of material must be used.
The Impact of Design on Manufacturing Processes
Analyzing existing components to verify that they are efficiently designed and manufactured may also yield considerable results. It is a methodology that focuses on optimizing the design of a product to improve its manufacturability and assembly, reducing production costs and improving the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process. Collaboration also helps to ensure that the product is designed with manufacturing in mind. By involving manufacturing teams in the design process, designers can gain valuable insights into the manufacturing process, allowing them to design products that are easy to manufacture.
DFMA
Other basics of effective DFM include standardisation of parts to save on part cost, design simplicity, which may reduce the complication or number of parts required, and setup time reduction. DFM principles can add value to product designs regardless of the industry by focusing on optimizing the design for ease of manufacturing. Whether it’s automotive, electronics, aerospace, or consumer goods, incorporating DFM tactics can streamline production processes, reduce costs, and improve product quality.
Shorter time to market
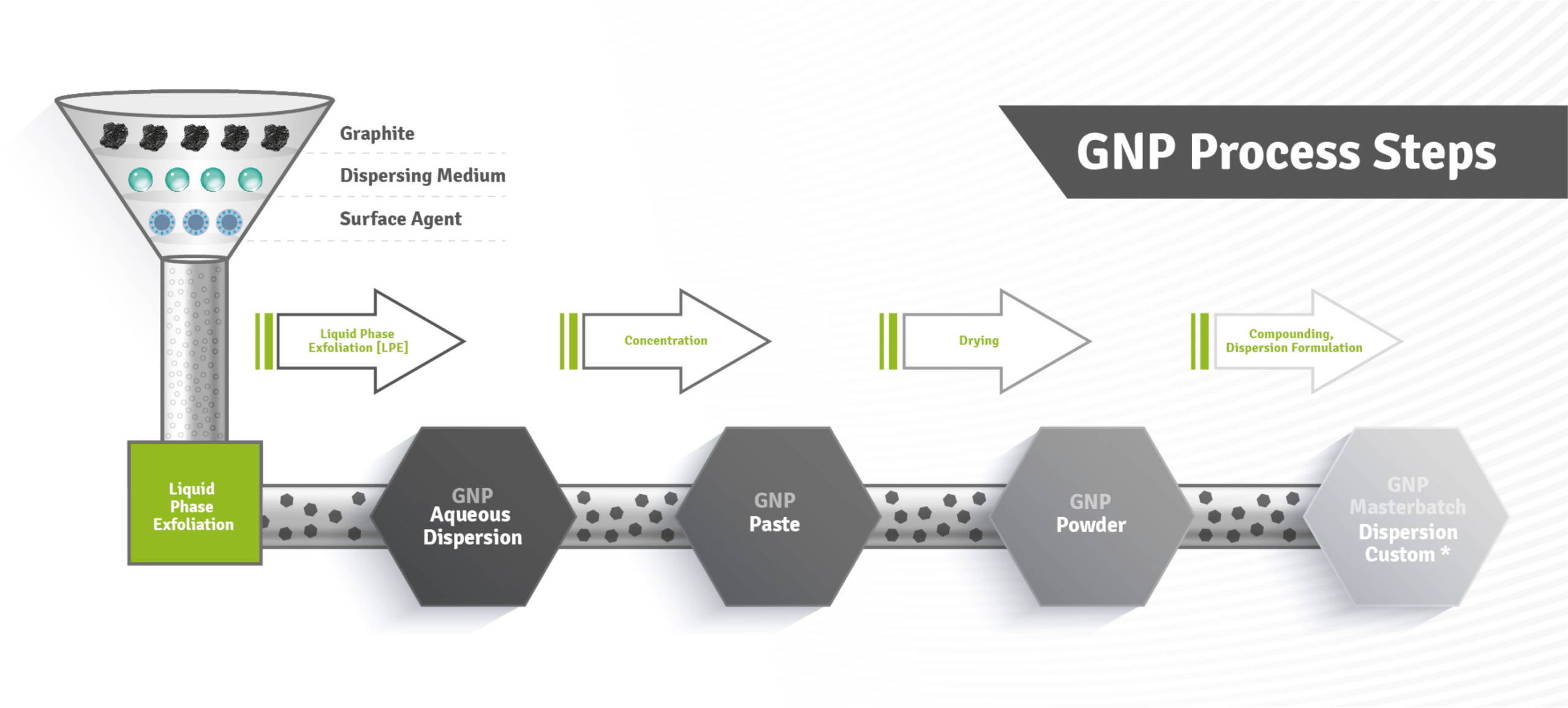
The primary difference between DFM and other conventional design methods is that DFM starts thinking about manufacturability at the conceptualization stage. No matter the product, a strategic DFM approach will always include all stakeholders. This ensures thorough consideration and planning of every aspect of the project. The current discussion about climate and pollution has once again brought to the fore the need for the world to change especially in the use of traditional products in manufacturing. Take advantage of our special offer and receive a free prototype with your next production order. It’s the perfect opportunity to test your design and make any necessary adjustments before moving forward with mass production.
PCB manufacturers must keep testing in mind during the design phase to avoid problems during manufacture. An inexpensive product won’t ever reach the market if it can’t meet its testing standards. Product design is crucial to applying DFM principles in PCB manufacture because even minor modifications can greatly affect product costs and lead times. For example, tolerances that are too loose result in an inferior product that increases machine costs without increasing the quality. Tolerances can greatly impact a PCB’s final production cost, so catching product errors early in manufacturing is essential.
Future of manufacturing heralds an AI-driven cloud-platform dream - Autodesk Redshift
Future of manufacturing heralds an AI-driven cloud-platform dream.
Posted: Mon, 20 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
This allows a manufacturer to identify and prevent mistakes or discrepancies. Design for Manufacturing is not merely an approach but a transformative philosophy that integrates the spheres of design and production, shaping them into a unified whole. By incorporating DFM best practices, businesses can anticipate and address potential manufacturing challenges during the product design phase, rather than reacting to them during production. This leads to significant cost savings, improved product quality, and shorter time to market. To overcome resource constraints, companies can prioritize DFM implementation by allocating additional time and budget to the design process. This can help to ensure that products are designed with manufacturing in mind, reducing production costs and improving overall quality.
What is Design for Manufacturability?
Manufacturability factors are integrated into DFM designs from the beginning, setting them apart from conventional techniques. Simplifying, improving, and refining the design to improve ease of manufacturing is the main focus of DFM, in contrast to traditional methods that prioritize functional elements. All manufacturing processes have limits on what is reasonable to manufacture — that's the gap between USL and LSL. Consult with your contract manufacturer or the trade organization for the process, if you are unsure. There is a lot of data on most common processes to give you guidance on what is reasonable to specify. A preliminary analysis should be performed once the conceptual design takes some shape to judge its base feasibility.
Following these guidelines, the final product should be easier to manufacture and the production should take less time when compared to the original design. In conclusion, DFM and DFA are both important approaches to product design that can help improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of the manufacturing process. However, DFM focuses on the entire manufacturing process, while DFA focuses on the assembly process.
Michaele Simmering studied at Brown University, while Johann Pauwen earned a degree in industrial design from the Rhode Island School of Art, and the husband-wife team's company marries their passions perfectly. And while the company's studio operates out of L.A., the couple works with Pennsylvanian craftspeople who utilize traditional techniques. Determining exactly the right design choices and trade-offs is largely dependent on scale, budget, and how important it is to preserve specific design intent. Watch our webinar to learn about five ways to use 3D printing in your manufacturing workflow. Design for manufacturability can be the domain of several manufacturing personas depending on the organizational context.
This has the potential to reduce the number of steps, materials, suppliers, glue, fasteners and total parts required to make a certain item. A well-designed product can be manufactured quickly and efficiently, while a poorly designed product may require additional steps or processes, leading to longer production times. In an era where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are the twin engines driving the manufacturing industry, Design for Manufacturing (DFM) has emerged as a key strategy to optimize both. The concept of DFM isn't new, but its relevance has been magnified by the increasing complexity of products and the relentless demand for higher quality and lower costs.

No comments:
Post a Comment